Abstract
Research Article
The pattern of blood pressure and renal function among children with Sickle Cell Anaemia presenting in a tertiary health institution in Nigeria
Adebukola Ajite*, Ezra Ogundare, Oludare Oluwayemi, Oladele Olatunya, Oluwasola Oke, Kayode Tolorunju and Evelyn Omoniyi
Published: 16 April, 2019 | Volume 3 - Issue 1 | Pages: 083-092
Background: In sickle cell anemia (SCA), compromise of the renal vasculature due to sickled red cells has been recognized.
Objectives: To assess the renal function and blood pressure pattern in children with sickle cell anaemia (SCA) presenting in a tertiary institution.
Method: A cross-sectional study of patients with sickle cell anaemia (SCA) over six months involving the use of questionnaires, general physical examination, blood pressure, investigations for haemoglobin genotype, urinalysis, serum creatinine, screening for hepatitis B and HIV.
Results: 51 children with SCA were seen. The prevalence of impaired renal function as defined by reduced eGFR <90mL/min/1.73m2 in this study was 27.5%, previous hospital admission and blood transfusion were associated with reduction in eGFR but blood pressure did not have significant correlation with the eGFR. The overall mean age at diagnosis of SCA was 4.09 ± 3.33 (years).
Conclusion: Impaired renal function is a major comorbid condition in children with SCA. In countries/locations where there is no newborn screening for sickle cell disease, diagnosis is delayed, thus detecting impaired renal function may be delayed, therefore the need for early detection and management is imperative.
Introduction
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001031 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
References
- Michael R, De Baun Elliott Vichinsky. Hemoglobinopathies: Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, RE Berman, RM Kliegman, HB Jenson, BF Stanton. 18th ed. Philadephia, 2007.
- Adekile AD, Adeodu O. Hemoglobinopathies. Paediatrics and child health in tropical region. 2nd ed 373-390.
- Guasch A, Cua M, Mitch WE. Early detection and the course of glomerular injury in patients with sickle cell anemia. Kidney Int. 1996; 49: 786-791. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/y3fz4nyh
- Guasch A, Cua M, You W, Mitch WE. Sickle cell anaemia causes a distinct pattern of glomerular dysfunction. Kidney Int. 1997; 51: 826-833. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/y3pd2mb5
- Serjeant GR, Serjeant BE. Sickle Cell Disease, 3rd ed. edn. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press. 2001; Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/y6qvjrdn
- Kadiri S. Chronic kidney disease: Sickle cell nephropathy as a likely cause. Annals of Ibadan Postgraduate Med. 2006; 4: 7-10.
- Day TG, Drasar ER, Fulford T, Sharpe CC, Thein SL. Association between hemolysis and albuminuria in adults with sickle cell anemia. Haematologica. 2012; 97: 201–205. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/y59xahlj
- Haymann JP, Stankovic K, Levy P, Avellino V, Tharaux PL, et al. Glomerular hyperfiltration in adult sickle cell anemia: a frequent hemolysis associated feature. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010; 5: 756–761. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/y27xrxyc
- Saborio P, Scheinman JI. Sickle cell nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999; 10: 187–192. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/y6jso6o6
- Guasch A. Primer on kidney disease, 4th edition. National Kidney Foundation. Sickle cell Nephropathy. 351-355.
- Johnson CS. Arterial blood pressure and hypervicosity in sickle cell disease. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2005; 19: 827-837. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/y3h3c6tb
- Johnson CS, Giorgio AJ. Arterial blood pressure in adults with sickle cell disease. Arch Intern Med. 1981; 141: 891-893. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/yygzykn2
- Grell GA, Alleyne GA, Serjeant GR. Blood pressure in adults with homozygous sickle cell disease. Lancet. 1981; 2: 1166. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/y5jl3w5s
- Pegelow CH, Colangelo L, Steinberg M, Wright EC, Smith J, et al. Natural history of blood pressure in sickle cell disease: risks for stroke and death associated with relative hypertension in sickle cell anemia. Am J Med. 1997; 102: 171-177. Ref.: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9217567
- Karayaylalí I, Onal M, Yíldízer K, Seyrek N, Paydas S, et al. Low blood pressure, decreased incidence of hypertension, and renal cardiac, and autonomic nervous system functions in patients with sickle cell syndromes. Nephron. 2002; 91: 535-537. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/y5vgcaep
- Hsien HC, Carvalhaes JTA, Braga JAP. Blood pressure in Children with sickle cell disease. Revista Paulista de Pedatria. 2012; 30: Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/y5ldc2sw
- De Miguel C, Speed JS, Kasztan M, Gohar EY, Pollock DM. Endothelin-1 and the kidney: new perspectives and recent findings. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016; 25: 35–41. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/y64e3kv3
- Falkner B, Daniels SR, Flynn JT, Gidding S, Green LA, et al. The Fourth Report on the Diagnosis, Evaluation and Treatment of High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics. 2004; 114: 555-576. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/y39b9fs6
- Schwatz GJ, Brion CP, Spitzer A. The use of plasma creatinine concentration for estimating GFR in infants, children and adolescents. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1987; 34: 571-590. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/yyah7644
- Epidemiology of Hb Disorders WHO. 2008; Weatherall DJ, Blood. 2010.
- Guasch A, Navarrete J, Nass K, Zayas CF. Glomerular involvement in adults with sickle cell hemoglobinopathies: Prevalence and clinical correlates of progressive renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006; 17: 2228-2235. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/y4xwh3fa
- Aneke JC, Adegoke AO, Oyekunle AA, Osho PO, Sanusi AA, et al. Degrees of Kidney Disease in Nigerian Adults with Sickle-Cell Disease. Med Princ Pract 2014; 23: 271-274. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/y3jt2hzp
- Rakhi P, Naik, Vimal K. Derebail. The spectrum of sickle hemoglobin-related nephropathy: from sickle cell disease to sickle trait. Expert Rev Hematol. 2007; 10: 12: 1087-1094. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/y5lpkxoz
- Vazquez B, Shah B, Zhang X, Lash JP, Gordeuk VR, et al. Hyperfiltration is associated with the development of microalbuminuria in patients with sickle cell anemia. Am J Hematol. 2014; 89: 1156–1157. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/y22p6p2j
- Sklar AH, Campbell H, Caruana RJ, Lightfoot BO, Gaier JG, et al. A population study of renal function in sickle cell anemia. Int J Artif Organs. 1990; 13: 231. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/y3gpvevp
- Falk RJ, Scheinman J, Phillips G, Orringer E, Johnson A, et al. Prevalence and pathologic features of sickle cell nephropathy and response to inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme. N Engl J Med. 1992; 326: 910-915. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/yyrr8nvs
- Yusuf R, Hassan A, Ibrahim I N, Babadoko AA, Ibinaiye PO. Assessment of kidney function in sickle cell anemia patients in Zaria, Nigeria. Sahel Med J. 2017; 20: 21-25. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/yxw9jw2j
- Heilbron DC, Holliday MA, al-Dahwi A, Kogan BA. Expressing glomerular filtration rate in children. Pediatr Nephrol.1991; 5: 5-11. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/y5x7v25v
- Olowu WA, Taiwo O, Oyelami A, Durosinmi MA, Adeodu OO, et al. Glomerular filtration rate in Nigerian children with homozygous sickle cell disease. Niger J Med. 2002; 11: 23-25. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/y56jut3l
- Ware RE, Rees RC, Sarnaik SA, Iyer RV, Alvarez OA, et al. BABY HUG Investigators. Renal function in infants with sickle cell anemia: baseline data from the BABY HUG trial. J Pediatr. 2010; 156: 66–70. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/y5p3xr3z
Figures:
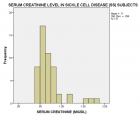
Figure 1

Figure 2

Figure 3
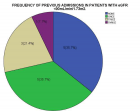
Figure 4
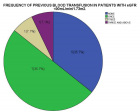
Figure 5
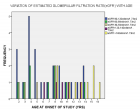
Figure 6
Similar Articles
-
The Risk-Adjusted Impact of Intraoperative Hemofiltration on Real-World Outcomes of Patients Undergoing Cardiac SurgeryMatata BM*,Shaw M. The Risk-Adjusted Impact of Intraoperative Hemofiltration on Real-World Outcomes of Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001001; 1: 001-010
-
Cardiac Manifestations on Anti-Phospholipid SyndromeFaisal AH*. Cardiac Manifestations on Anti-Phospholipid Syndrome. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001002; 1: 011-013
-
Intraperitoneal and Subsequent Intravenous Vancomycin: An Effective Treatment Option for Gram-Positive Peritonitis in Peritoneal DialysisBarone RJ*,Gimenez NS,Ramirez L. Intraperitoneal and Subsequent Intravenous Vancomycin: An Effective Treatment Option for Gram-Positive Peritonitis in Peritoneal Dialysis. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001003; 1: 014-018
-
Acute Tubulointerstitial Nephritis due to Phenytoin: Case ReportNilzete Liberato Bresolin*,Pedro Docusse Junior,Maria Beatriz Cacese Shiozawa,Marina Ratier de Brito Moreira,Natalia Galbiatti Silveira. Acute Tubulointerstitial Nephritis due to Phenytoin: Case Report. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001004; 1: 019-025
-
Profile of vitamin D receptor polymorphism Bsm I and FokI in end stage renal disease Egyptian patients on maintenance hemodialysisEL-Attar HA*,Mokhtar MM,Gaber EW. Profile of vitamin D receptor polymorphism Bsm I and FokI in end stage renal disease Egyptian patients on maintenance hemodialysis. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001005; 1: 026-040
-
Anemia response to Methoxy Polyethylene Glycol-Epoetin Beta (Mircera) versus Epoetin Alfa (Eprex) in patients with chronic Kidney disease on HemodialysisAlaa K Dhayef*,Jawad K Manuti,Abdulwahab S Abutabiekh. Anemia response to Methoxy Polyethylene Glycol-Epoetin Beta (Mircera) versus Epoetin Alfa (Eprex) in patients with chronic Kidney disease on Hemodialysis. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001006; 1: 041-047
-
The outcome of Acute Kidney Injury in patients with severe MalariaJoão Egidio Romão Jr*,João Alberto Brandão. The outcome of Acute Kidney Injury in patients with severe Malaria. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001007; 1: 048-054
-
Short term effect of Intravenous Intermittent Iron Infusion versus Bolus Iron Infusion on Iron parameters in Hemodialysis patientsIman Ibrahim Sarhan,Hussein Sayed Hussein,Islam Omar Elshazly*,Mahmoud Salah Hassan. Short term effect of Intravenous Intermittent Iron Infusion versus Bolus Iron Infusion on Iron parameters in Hemodialysis patients. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001008; 1: 055-059
-
Association between bh4/bh2 ratio and Albuminuria in Hypertensive Type -2 Diabetic patientsJose Aviles-Herrera,Karla C Arana-Pazos,Leonardo Del Valle-Mondragon,Carolina Guerrero-García,Alberto Francisco Rubio-Guerra*. Association between bh4/bh2 ratio and Albuminuria in Hypertensive Type -2 Diabetic patients. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001009; 1: 060-063
-
Posterior Reversible Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome in a patient after second dose of Rituximab for treatment of resistant Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic PurpuraSabaa Asif*,Sumbal Nasir Mahmood,Osama Kunwer Naveed. Posterior Reversible Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome in a patient after second dose of Rituximab for treatment of resistant Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura . . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001010; 2: 001-004
Recently Viewed
-
Various Theories of Fast and Ultrafast Magnetization DynamicsManfred Fähnle*. Various Theories of Fast and Ultrafast Magnetization Dynamics. Int J Phys Res Appl. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijpra.1001101; 7: 154-158
-
Forest History Association of WisconsinEd Bauer*. Forest History Association of Wisconsin. J Radiol Oncol. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jro.1001071; 8: 093-096
-
Synthesis of Carbon Nano Fiber from Organic Waste and Activation of its Surface AreaHimanshu Narayan*,Brijesh Gaud,Amrita Singh,Sandesh Jaybhaye. Synthesis of Carbon Nano Fiber from Organic Waste and Activation of its Surface Area. Int J Phys Res Appl. 2019: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijpra.1001017; 2: 056-059
-
Obesity Surgery in SpainAniceto Baltasar*. Obesity Surgery in Spain. New Insights Obes Gene Beyond. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.niogb.1001013; 4: 013-021
-
Tamsulosin and Dementia in old age: Is there any relationship?Irami Araújo-Filho*,Rebecca Renata Lapenda do Monte,Karina de Andrade Vidal Costa,Amália Cinthia Meneses Rêgo. Tamsulosin and Dementia in old age: Is there any relationship?. J Neurosci Neurol Disord. 2019: doi: 10.29328/journal.jnnd.1001025; 3: 145-147
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."