Abstract
Case Report
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) in a 76-year old woman presenting with pulmonary nodule and accelerating acute kidney injury
Noor Sameh Darwich*, Melissa Schnell and L. Nicholas Cossey
Published: 20 January, 2020 | Volume 4 - Issue 1 | Pages: 001-006
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), a form of ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV), is a rare disease with an often-occult presentation. It is more common in 4th and 5th decades of life but can be seen in all ages.
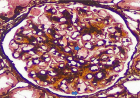
This case report details a 76-year-old female presenting with abdominal pain, generalized weakness, and malaise, who was found to have pulmonary nodules on chest imaging. Biopsy of the lung nodule showed organizing pneumonia. Initially, antibiotics were used to treat the patient. However, she developed acute renal failure a few days after presentation and found to have positive serum C-ANCA as well as elevated ANCA-PR3 serologies. A subsequent kidney biopsy demonstrated pauci-immune necrotizing and crescentic glomerulonephritis that was consistent with GPA and the patient was started immediately on combination immunosuppressive therapy, plasmapheresis, and hemodialysis.
GPA’s clinical and radiological presentation can mimic other common conditions such as pneumonia, malignancy, bacterial sinusitis, pulmonary tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, and urinary tract infection. Because of this, a high level of suspicion is required for early diagnosis and treatment to alter the high mortality rate in this disease entity. All forms of ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) should be in the differential diagnosis for all patients presenting with multiorgan system involvement particularly in individuals with pulmonary and renal manifesations.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001048 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
GPA; ANCA-associated Vasculitides (AAV); Wegener granulomatosis
References
- Falk RJ, Gross WL, Guillevin L, Hoffman GS, Jayne DR, et al. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s): an alternative name for Wegener’s granulomatosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011; 63: 863-864. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21374588
- Seo P, Stone JH. The antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Am J Med. 2004; 117: 39-50. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15210387
- Gomez-Puerta JA, Hernandez-Rodriguez J, Lopez-Soto A, Bosch X. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitides and respiratory disease. Chest 2009; 136: 1101-1111. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19809051
- Jayne D. The diagnosis of vasculitis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol.. 2009; 23: 445-453. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19508950
- Sedighi S, Aghaie M, Mozafari N, Roshandel G. Different features in Wegener’s Granulomatosis: report of five cases. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research. 2011(Suppl-2), 5:1437-1439.
- Specks U, Merkel PA, Seo P, Spiera R, Langford CA, et al. Efficacy of remission-induction regimens for ANCA- associated vasculitis. N Eng J Med. 2013; 369: 417-427. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23902481
- Jayne DR, Gaskin G, Rasmussen N, Abramowicz D, Ferrario F, et al. Randomized trial of plasma exchange or High-dose methylprednisolone A adjunctive therapy for sever renal vasculitis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007; 18: 2180-218. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17582159
- Langford CA, Hoffman GS. Wegener’s granulomatosis. Thorax 1999; 54: 629-637. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1745525/
- Shafiei K, Luther E, Archie M, Gulick J, Fowler MR. Wegener’s granulomatosis: Case report and brief literature review. J Am Board Fam Pract. 2003; 16: 555-559. PubMed:
- Sfiniadaki E, Tsiara I, Theodossiadis P, Chatziralli I. Ocular manifestations of Granulomatosis polyangiitis: A review of the Literature. Ophthalmol Ther (2019) 8:227-234. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14963084
- Stewart C, Cohen D, Bhattacharyya I, Scheitler L, Riley S, et al. Oral manifestations of Wegener’s granulomatosis: a report of three cases and literature review. J Am Dent Assoc. 2007; 138: 338-348. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17332039
- Storesund B, Gran JT, Koldingsnes W. Severe intestinal involvement in wegener’s granulomatosis: report of two cases and review of the literature. Br J Rheumatol. 1998; 37: 387-390. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9619888
- Pagnoux C, Mahr A, Cohen P, Guillevin L. Presentation and outcome of gastrointestinal involvement in systemic necrotizing vasculitidies: analysis of 62 patients with polyarteritis nodosa, microscopic polyangiitis, Wegener granulomatosis, Churg-Strauss syndrome, or rheumatoid arthritis-associated vasculitis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2005; 84: 115128. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15758841
- Miller PG, Santini C, Freed MJ. Dysphagia in a patient with Wegener's Granulomatosis: a Case report. Dysphagia. 2001; 16: 136-139. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11305224
- Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon PA, Basu N, Cid MC, et al. 2012 revised international chapel Hill onsensus conference Nomenclature of vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2013; 65: 1-11. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23045170
- Roth AJ, Ooi JD, Hess JJ, van Timmeren MM, Berg EA, et al. Epitope specificity determines pathogenicity and detectability in ANCA-associated vasculitis. J Clin Invest. 2013; 123: 1773-1783. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23549081
- Schnabel A, Holl-Ulrich K, Dalhoff K, Reuter M, Gross WL. Efficacy of transbronchial biopsy in pulmonary vasculitidies. Eur Respir J. 1997; 10: 2738-2743. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9493653
- Rovin BH, Caster DJ, Cattran DC, Gibson KL, Hogan JJ, et al. Management and treatment of glomerular Diseases (part 2): conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) controversies conference. Kidney Int. 2019; 95: 281-295; PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30665569
- Yates M, Watts RA, Bajema IM, Cid MC, Crestani B, et al. EULAR/ERA-EDTA recommendations for the Management of ANCA-associated vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis 2016; 75: 1583-1594. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27338776
- Tesar V, Rihova Z, Jancova E, Rysava R, Merta M, et al. Current treatment strategies in ANCA-positive renal vasculitis: lessons from European randomized trials. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003; 18: Suppl 5: V2-V4. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12817056
- Charles P, Néel A, Tieulié N, Hot A, Pugnet G, et al. Rituximab for induction and maintenance treatment of ANCA-Associated vasculitides: a multicenter retrospective study on 80 patients. Rheumatology. 2014; 53: 532-539. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24282319
- Getha D, Kallenberg C, Stone JH, Salama AD, Appel GB, et al. Current therapy of Granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic Polyangiitis: the role of rituximab. J Nephrol. 2015; 28: 17-27. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25185728
- Merkel PA, Kaplan AA, Falk RJ, Granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic Polyangiitis: intial immunosuppressive therapy. UpToDate. 2020; 1-37.
- Jones RB, Furuta S, Tervaert JW. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide in ANCA-Associated renal vasculitis: 2-year results of a randomized trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015; 74: 1178-1182. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25739829
- Klemmer PJ, Chalermskulrat W, Reif MS, Hogan SL, Henke DC, et al. Plasmapheresis therapy for diffuse alveolar hemorrhage in patients with small-vessel vasculitis. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2003; 42: 1149-1153. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14655185
- Walsh M, Merkel PA, Jayne. The Effects of Plasma Exchange and reduced-Dose Glucocorticoids during Remission-Induction for Treatment of Sever ANCA-Associated Vasculitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018: 70 (Suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effects-of-plasma-exchange-and-reduced-dose-glucocorticoids-during-remission-induction-for-treatement-of-sever-anca-associated-vasculitis/
- Hogan SL, Folk RJ, Chin H, Cai J, Jennette CE, et al. Predictors of relapse and treatment resistance in Antineurtophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Small-vessel Vasculitis. Ann Intern Med. 2005; 143: 621-631. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16263884
- Popa ER, Trevaert JW. The relation between Staphylococcus aureus and Wegener’s Granulomatosis: Current knowledge and future Directions. Intern Med. 2003; 42: 771-780. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14518661
- Stegeman CA, Tervaert JW, de Jong PE, Kallenberg CG. Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole(CO-TRIMOXAZOLE) for the prevention of relapses of Wegener’s granulomatosis. For the Dutch Co-Trimoxazole Wegener Study group. N Engl J Med. 1996; 335: 16-20. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8637536
- Geetha D, Jefferson JA. ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: Core Curriculum 2020. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020; 75: 124-137. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31358311
- Jayne DRW, Bruchfeld AN, Harper L, Schaier M, Venning MC, et al. CLEAR study Group. Randomized trial of C5a Receptor inhibitor Avocopan in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. J AM Soc nephrol. 2017; 28: 2756-2767. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28400446
- Salvadori M, Tsalouchos A. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody associated Vasculitides with renal involvement: Open challenges in the remission induction Therapy. World J nephrol. 2018; 7: 71-83. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29736379
Figures:
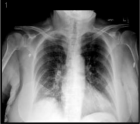
Figure 1
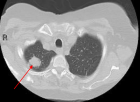
Figure 2
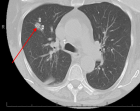
Figure 3
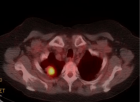
Figure 4
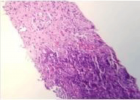
Figure 5
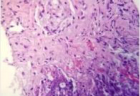
Figure 6
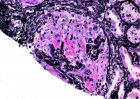
Figure 7
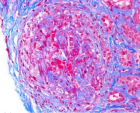
Figure 8
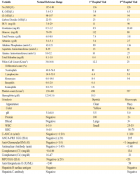
Figure 9
Similar Articles
-
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) in a 76-year old woman presenting with pulmonary nodule and accelerating acute kidney injuryNoor Sameh Darwich*,Melissa Schnell,L. Nicholas Cossey. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) in a 76-year old woman presenting with pulmonary nodule and accelerating acute kidney injury. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001048; 4: 001-006
Recently Viewed
-
Improvement of the Cognitive Abilities in a Chronic Generalized Anxiety Disorder and Moderate Depression Case using a Novel Integrated Approach: The Cognitome ProgramMohita Shrivastava*. Improvement of the Cognitive Abilities in a Chronic Generalized Anxiety Disorder and Moderate Depression Case using a Novel Integrated Approach: The Cognitome Program. J Neurosci Neurol Disord. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jnnd.1001100; 8: 069-089
-
Neuroprotective Effect of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone in a Mouse Model of HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorder (HAND)Tapas K Makar, Joseph Bryant, Bosung Shim, Kaspar Keledjian, Harry Davis, Manik Ghosh, Ajay Koirala, Ishani Ghosh, Shreya Makar, Alonso Heredia, Malcolm Lane, J Marc Simard, Robert C Gallo, Volodymyr Gerzanich*, Istvan Merchenthaler*. Neuroprotective Effect of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone in a Mouse Model of HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorder (HAND). J Neurosci Neurol Disord. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jnnd.1001101; 8: 090-105
-
Adult Neurogenesis: A Review of Current Perspectives and Implications for Neuroscience ResearchAlex, Gideon S*,Olanrewaju Oluwaseun Oke,Joy Wilberforce Ekokojde,Tolulope Judah Gbayisomore,Martina C. Anene-Ogbe,Farounbi Glory,Joshua Ayodele Yusuf. Adult Neurogenesis: A Review of Current Perspectives and Implications for Neuroscience Research. J Neurosci Neurol Disord. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jnnd.1001102; 8: 106-114
-
Analysis of Psychological and Physiological Responses to Snoezelen Multisensory StimulationLucia Ludvigh Cintulova,Jerzy Rottermund,Zuzana Budayova. Analysis of Psychological and Physiological Responses to Snoezelen Multisensory Stimulation. J Neurosci Neurol Disord. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jnnd.1001103; 8: 115-125
-
Sexual Dimorphism in the Length of the Corpus Callosum in CadaverShahnaj Pervin*,Nasaruddin A,Irfan M,Annamalai L. Sexual Dimorphism in the Length of the Corpus Callosum in Cadaver. J Neurosci Neurol Disord. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jnnd.1001104; 8: 126-129
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."