Figure 2
SGLT2 Inhibitors and nephroprotection in diabetic kidney disease: From mechanisms of action to the latest evidence in the literature
Jorge Rico-Fontalvo, Rodrigo Daza-Arnedo, Maria Ximena Cardona-Blanco, Victor Leal-Martínez, Emilio Abuabara-Franco, Nehomar Pajaro-Galvis*, Jose Cabrales, José Correa, Manuel Cueto, Amable Duran, Alejandro Castellanos, Javier Enamorado, José Bohórquez, Isabella Uparella, Julio Zuñiga, Abraham Chagui, Alfonso Ramos and Luis Lara
Published: 21 August, 2020 | Volume 4 - Issue 2 | Pages: 044-055
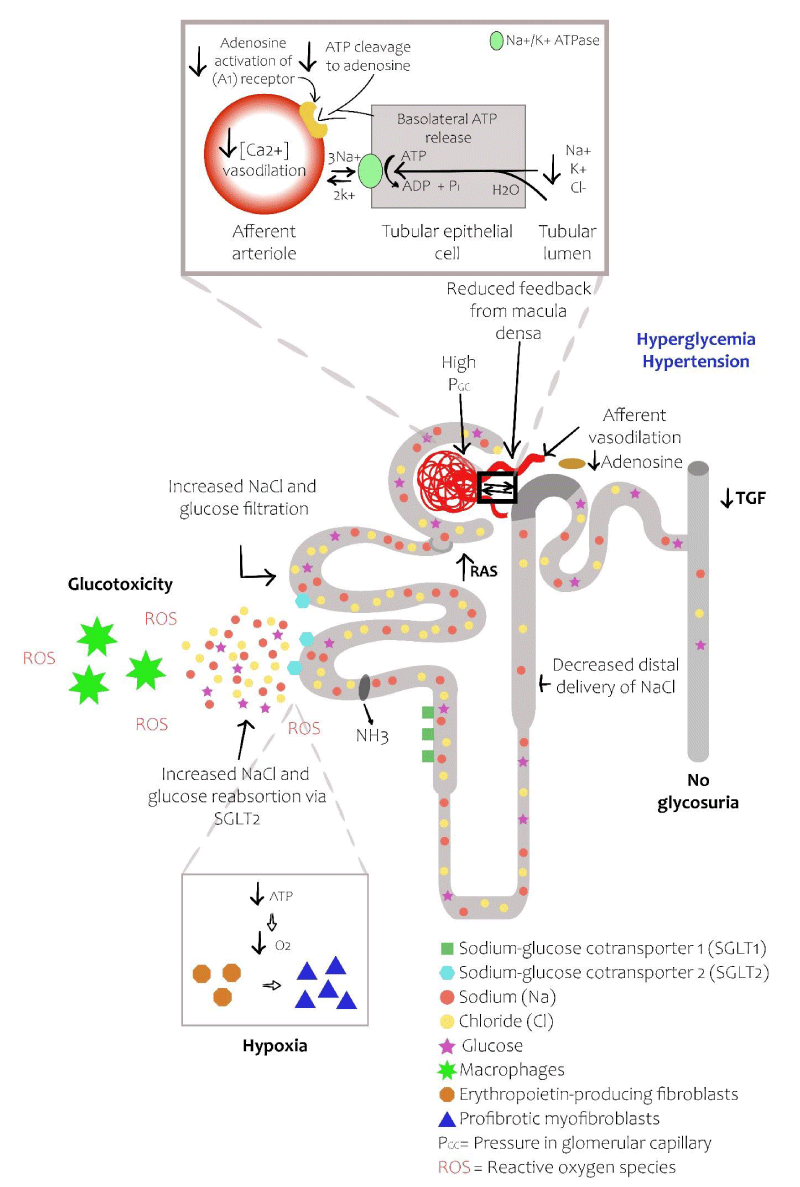
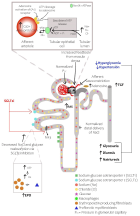
Figure 2:
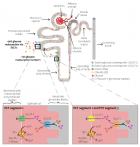
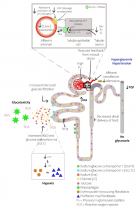
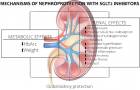
Diabetic nephron. The increase in reabsorption of glucose by SGLT2 in the proximal convoluted tubule decreases the delivery of solutes to the macular density. The resulting decrease in ATP release from the basolateral membrane of the epithelial tubular cells reduces the production of adenosine produces vasodilatation of the afferent arteriole, leading to hyperfiltration and an increase in the glomerular capillary pressure. The increase infiltrate glucose produces inflammation and oxidative stress. Finally, the increase in oxygen consumption of the renal cortex can contribute to renal fibrosis by inducing hypoxia and differentiation of EPO producing fibroblasts in pro-fibrotic myofibroblasts (adapted from references 3 and 5).
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001058 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
More Images
Similar Articles
-
Anemia response to Methoxy Polyethylene Glycol-Epoetin Beta (Mircera) versus Epoetin Alfa (Eprex) in patients with chronic Kidney disease on HemodialysisAlaa K Dhayef*,Jawad K Manuti,Abdulwahab S Abutabiekh. Anemia response to Methoxy Polyethylene Glycol-Epoetin Beta (Mircera) versus Epoetin Alfa (Eprex) in patients with chronic Kidney disease on Hemodialysis. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001006; 1: 041-047
-
Complete recovery of chronic Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome with plasma exchangeSumbal Nasir Mahmood*,Kunwer Naveed Mukhtar,Osama Kunwer Naveed,Ahmed Kunwer Naveed. Complete recovery of chronic Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome with plasma exchange. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001011; 2: 005-007
-
A case report of Hypocomplementemic urticarial vasculitic syndrome presenting with Renal failureAmy M Hopkins,Angela M Gibbs,Ryan S Griffiths,Rupali S Avasare,Firas G Khoury*. A case report of Hypocomplementemic urticarial vasculitic syndrome presenting with Renal failure. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001017; 2: 039-043
-
Relationship between Fetuin-A and vascular or valvular calcification in hemodialysis patientsShahrzad Ossareh*,Bahareh Marghoob,Robabeh Bayat. Relationship between Fetuin-A and vascular or valvular calcification in hemodialysis patients. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001021; 3: 001-011
-
Chronic kidney disease in women: a cross sectional screening in a tertiary care hospital in VaranasiRai Pradeep K*,Rai Punam,Bedi Sonam. Chronic kidney disease in women: a cross sectional screening in a tertiary care hospital in Varanasi . . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001022; 3: 012-018
-
Anti-Inflammatory probiotic biomarkers in Fermented foodsFarid E Ahmed*,Nancy C Ahmed . Anti-Inflammatory probiotic biomarkers in Fermented foods . . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001023; 3: 019-041
-
Chronic Kidney Disease: A single day screening on World Kidney Day for five consecutive yearsRai Pradeep K*,Rai Punam,Bedi Sonam. Chronic Kidney Disease: A single day screening on World Kidney Day for five consecutive years. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001025; 3: 046-054
-
Challenges of haemodialysis: A single centre experience in South West NigeriaSamuel Ayokunle Dada*,Adebukola Bidemi Ajite,Funmilayo Abimbola Ibitoba,Awolowo Anthony Thomas,Oluwamayowa Esther Dada,Olabisi Olamide Deji-Dada. Challenges of haemodialysis: A single centre experience in South West Nigeria . . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001026; 3: 055-060
-
Anti-glomerular basement membrane disease: A case report of an uncommon presentationNatália Silva*,Luís Oliveira,Mónica Frutuoso,Teresa Morgado. Anti-glomerular basement membrane disease: A case report of an uncommon presentation. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001027; 3: 061-065
-
Peritonitis: Culprit for peritoneal dialysis declineKishore Kumar*,Jais Kumar,Chaudhri Naureen. Peritonitis: Culprit for peritoneal dialysis decline . . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcn.1001028; 3: 066-070
Recently Viewed
-
Impact of Latex Sensitization on Asthma and Rhinitis Progression: A Study at Abidjan-Cocody University Hospital - Côte d’Ivoire (Progression of Asthma and Rhinitis related to Latex Sensitization)Dasse Sery Romuald*, KL Siransy, N Koffi, RO Yeboah, EK Nguessan, HA Adou, VP Goran-Kouacou, AU Assi, JY Seri, S Moussa, D Oura, CL Memel, H Koya, E Atoukoula. Impact of Latex Sensitization on Asthma and Rhinitis Progression: A Study at Abidjan-Cocody University Hospital - Côte d’Ivoire (Progression of Asthma and Rhinitis related to Latex Sensitization). Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001035; 8: 007-012
-
Olfactory Dysfunction in Sports Players following Moderate and Severe Head Injury: A Possible Cut-off from Normality to PathologyGesualdo M Zucco*,Andrea Carletti,Richard J Stevenson. Olfactory Dysfunction in Sports Players following Moderate and Severe Head Injury: A Possible Cut-off from Normality to Pathology. J Sports Med Ther. 2016: doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001001; 1: 001-005
-
Emerging Trends in Sports Cardiology: The Role of Micronutrients in Cardiovascular Health and PerformanceBiswajit Sharma, Kishore Mukhopadhyay*. Emerging Trends in Sports Cardiology: The Role of Micronutrients in Cardiovascular Health and Performance. J Sports Med Ther. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001086; 9: 073-082
-
Transforming Cancer Care through Physical Exercise: A Path to Holistic HealingJorma Sormunen*. Transforming Cancer Care through Physical Exercise: A Path to Holistic Healing. J Sports Med Ther. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001088; 9: 089-090
-
Hypochlorous acid has emerged as a potential alternative to conventional antibiotics due to its broad-spectrum antimicrobial activityMaher M Akl*. Hypochlorous acid has emerged as a potential alternative to conventional antibiotics due to its broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity. Int J Clin Microbiol Biochem Technol. 2023: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcmbt.1001026; 6: 001-004
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."