Table of Contents
A Case of Rapidly Progressive Renal Failure with Unearthed Amyloidosis
Published on: 4th February, 2025
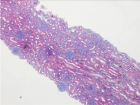
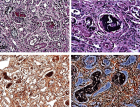
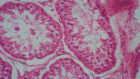
Amyloidosis-associated kidney disease commonly manifests with chronic glomerular symptoms including heavy proteinuria predominantly albuminuria. Clinical presentation ranges from full-blown nephrotic syndrome, hematuria, and hypertension to renal failure. In India patients with chronic kidney disease are mainly attributed to hypertension and diabetes but an underlying etiology such as amyloidosis needs to be unearthed and shouldn’t be ignored as an etiology. We report a case of a 60-year-old man with hypertension and hypothyroidism who presented with frothy urine for several years, b/l pedal edema for 15 days. Over the past 3 months, there was a serial increase in creatinine. As per CKD-EPI equation, the patient was CKD-4. As the patient was suspected to be rapidly progressive renal failure; a renal biopsy was planned. Biopsy reports were suggestive of Amyloidosis. Glomerular, vascular, and tubulointerstitial deposition of amyloid was seen. Based on renal biopsy and IHC staining; the patient’s diagnosis was AA-associated secondary renal amyloidosis. Thus in this case renal amyloidosis was an unearthed etiology.
Gallstone Ileus: A Rare Case of Intestinal Obstruction, Presented in a Chronic Kidney Disease Patient on Haemodialysis
Published on: 5th February, 2025
The prevalence of gallbladder stones is higher in Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) patients and it has been shown to increase with the advancement of the disease stage, from 7.7% in stage 1% to 21.3% in stage 5. Gallstone ileus is a rare complication which presents in just 0.3% - 0.5% of patients with cholelithiasis. A 61-year-old female patient, with a known case of CKD on maintenance hemodialysis, (thrice a week) with primary disease of hypertensive and diabetic nephropathy; presented with multiple episodes of loose stool, vomiting, and diffuse abdominal pain for 2 days. Abdomen Ultrasonography (USG) was suggestive of intestinal obstruction. CT abdomen with oral contrast revealed grossly dilated jejuna loops with air-fluid levels and transition zone in the pelvis, in distal jejunal loops/proximal ileum with ovoid intraluminal filling defect cystic polyp and collapsed bowel loops. The patient underwent exploratory laparotomy in view of persistent small bowel obstruction. Resection and anastomosis of the mass-bearing small bowel segment were performed. On cutting and opening the specimen, a large stone was revealed. This gallstone was causing bowel obstruction-gall stone ileus. A gallstone 2.6 cm x 2.1 cm has traversed through a cholecysto-duodenal fistula and got stuck in the proximal ileum, causing small bowel obstruction. The lesson learned is uraemia can cause gastrointestinal symptoms like anorexia, abdominal pain, vomiting, and ileus and hence mimic serious differentials of the acute abdomen like gallstone ileus. Thus no stone should be left unturned especially when the prevalance of gallstones is high in chronic kidney disease patients.
Unmasking Renal Complications of Immunotherapy: A Case of Nivolumab-induced FSGS
Published on: 7th February, 2025
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (ICPIs), while revolutionizing cancer therapy through potentiation of anti-tumour responses via targeted blockade of T-lymphocyte inhibitory receptors, are associated with immune-related adverse events (irAEs), including diverse renal manifestations. This report presents a case of a 69-year-old male with urothelial carcinoma who developed Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) and nephrotic-range proteinuria following initiation of nivolumab, an anti-PD1 antibody, necessitating renal biopsy to clarify the aetiology. The biopsy revealed Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) with endotheliopathy, suggesting a direct ICPI-induced glomerular injury. This case underscores the need for heightened awareness of ICPI-associated glomerular disease, alongside more common renal adverse events such as Acute Interstitial Nephritis (AIN), and for the need for renal biopsy in such cases. While the incidence of ICPI-associated AKI is approximately 17%, and AIN is a more frequent finding, FSGS and other glomerular pathologies should also be considered. Current treatment for such renal events involves discontinuation of the ICPI agent and initiation of immunosuppression with glucocorticoids. The management of these cases requires prompt detection, timely diagnosis, and often interdisciplinary collaboration, thus highlighting the need for more case reports, research, and better treatment strategies.

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."